Performance Optimization Practice
Data preparation
Below are structures of data tables used in this handbook:
| Table | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Categories | [CategoryID] [int] NOT NULL, [CategoryName] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Description] [nvarchar](100) NULL |
Category ID Category name Category description |
| Customers | [CustomerID] [nvarchar](10) NOT NULL, [CustomerName] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [ContactName] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [ContactTitle] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Address] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [City] [nvarchar](20) NULL, [Region] [nvarchar](20) NULL, [PostalCode] [nvarchar](20) NULL, [Country] [nvarchar](20) NULL, [Phone] [nvarchar](30) NULL, [Fax] [nvarchar](30) NULL |
Customer ID Customer name Contact Contact title Customer address City Region Postal code Country Telephone Fax |
| Employees | [EmployeeID] [int] NOT NULL, [LastName] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [FirstName] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Title] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [TitleOfCourtesy] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Birthday] [date] NULL, [HireDate] [date] NULL, [Address] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [City] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Region] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [PostalCode] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Country] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [HomePhone] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Gender] [nvarchar](50) NULL |
Employee ID Last name First name Title Courtesy title Birthday Hire date Address City Region Postal code Country Home phone Gender |
| Orders | [CustomerID] [nvarchar](10) NULL, [OrderDate] [datetime] NULL, [ProductID] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [Quantity] [int] NULL, [Unit] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Price] [decimal](18, 2) NULL, [Amount] [decimal](18, 2) NULL, [EmployeeID] [int] NULL, [EmployeeName] [string] NULL, [ShipVia] [nvarchar](20) NULL |
Customer ID Order date Product ID Quantity Unit Unit price Amount of money Employee ID Employee name Means of transportation |
| Products | [ProductID] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [ProductName] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL, [SupplierID] [int] NULL, [CategoryID] [int] NULL, [QuantityPerUnit] [nvarchar](20) NULL, [UnitPrice] [decimal](18, 2) NULL |
Product ID Product name Supplier ID Category ID Quantity per unit Unit price |
| Suppliers | [SupplierID] [int] NOT NULL, [CompanyName] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [ContactName] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [ContactTitle] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Address] [nvarchar](100) NULL, [City] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Region] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [PostalCode] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Country] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Phone] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Fax] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [HomePage] [nvarchar](100) NULL |
Supplier ID Supplier name Contact name Contact title Address City Region Postal code Country Telephone Fax Website |
| Areas | [Country] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Region] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [City] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [CityName] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [PostalCode] [nvarchar](50) NULL |
Country Region City City name Postal code |
Relationships between tables:
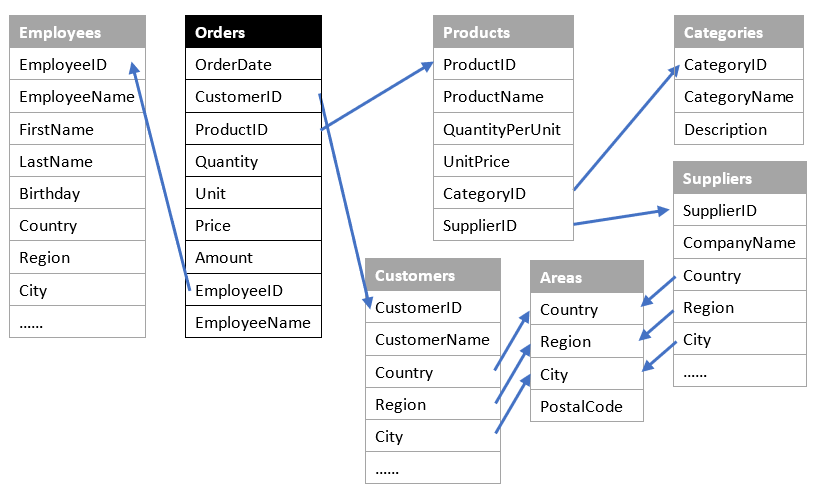
As databases lack generality, we use text files to store the test data. Small data tables are directly stored in files, and large data tables can be generated based on script below.
Table of contents
1 Using file storage
1.1 Bin file
1.2 Composite table
1.3 Converting date to small integer
1.4 Conversion from enumerated string to small integer
2 Understanding aggregation
2.1 COUNT DISTINCT
2.2 DISTINCT
2.3 Getting record(s) containing the max/min value
2.4 Getting top/bottom N values
2.5 Getting records containing top/bottom N
2.6 When there is a redundant grouping field
2.7 Getting the first/last record from each group
3 Order-based storage
3.1 Storing data in time order
3.2 Order-based filtering
3.3 Storing data in account order
3.4 Order-based DISTINCT
3.5 Order-based COUNT DISTINCT
3.6 Order-based grouping & summarization
3.7 Getting the first/last record from each group
3.8 Complicated judgment on each group
4 Dimension table pointed by foreign key
4.1 Storing dimension table in memory
4.2 Computations on a dimension table
4.3 Wide table
4.4 Numberized dimension table
4.5 Filtering on dimension table
4.6 Alignment sequence
4.7 Temp dimension table and segmented dimension table
4.8 External memory dimension table
5 Primary-key-based Association
5.1 Order-based merge
5.2 Computing intersection and union
5.3 Filtering sub table according to primary table
5.4 Filtering primary table according to sub table
6 Multi-purpose traversal
6.1 Basic concept
6.2 Application scenarios
7 Search tasks
7.1 Equivalent value Search
7.2 Interval-based search
7.3 Batch search
7.4 Full-text index
SPL Official Website 👉 https://www.scudata.com
SPL Feedback and Help 👉 https://www.reddit.com/r/esProcSPL
SPL Learning Material 👉 https://c.scudata.com
SPL Source Code and Package 👉 https://github.com/SPLWare/esProc
Discord 👉 https://discord.gg/2bkGwqTj
Youtube 👉 https://www.youtube.com/@esProc_SPL



Chinese version